In the Matter of Minority Physics Students v. Chief Justice Roberts
On December 9, 2015, Chief Justice Roberts asked the question "What unique perspective does a minority student bring to a physics class?" during the discussion of a case on affirmative action at the university level. It appears that he chose a physics class because he felt that this discipline definitely does not need diverse perspectives. As a female physicist who has been teaching at the University of Pittsburgh for two decades, I feel that the Chief Justice’s question suggests a lack of familiarity with urgent issues in education that must be addressed to maintain U.S. competitiveness.


The question first implies that it is the perspective of the minority student that is the critical feature rather than the presence of the minority student in the physics class. We need to attract minority students to disciplines that need their talents. Currently, approximately 20 percent of undergraduate and Ph.D. students in physics programs across the U.S. are females, which is significantly lower than the percentage in many European and Asian countries. What is perhaps more alarming is that only about 9 percent of physics undergraduate degrees and 6 percent of Ph.D. degrees are awarded to students from underrepresented races and ethnicities. According to the AIP Statistical Research Center, while the number of students obtaining a bachelor’s degree in physics increased by 58 percent from 2003-2013, the increase for the African-American students was only 1 percent. In addition, the minority population is projected to become the majority in the U.S. in a few decades. The students from the minority groups are often from economically disadvantaged families, who are often denied the opportunities to get ahead that children from families without economic concerns typically receive. Moreover, there are other barriers due to societal stereotypes and implicit bias that impact the advancement of various underrepresented groups in physics including women and those from underrepresented races and ethnicities. There is an urgent need to engage and increase the participation of these traditionally underrepresented students, whose talents in physics have largely been untapped. These students will be attracted to the beauty of physics if they are supported and encouraged early and often, and have role models.
In response to the Chief Justice’s question, the APS President Sam Aronson released a statement on diversity which notes, “One physics student from a minority community disparaged and feared at the time — the Jews of 19th century Germany — was Albert Einstein, whose unique perspective transformed the world.” One of my colleagues, who was a Ph.D. student of Manhattan Project leader J. Robert Oppenheimer, told me that he had wanted to major in math but the chairman of the math department at the time blatantly told him and others that Jewish students majoring in math would not find decent math related jobs. Therefore, he majored in physics! Although one may feel relieved now that we do not have this level of explicit discrimination against underrepresented groups, it is important to understand that stereotypes and implicit biases persist and can negatively impact the advancement of underrepresented groups.
My two children attended a public high school in which half of the students were African American, Hispanic, or multi-racial and the other half were white. This school appeared to be “well-integrated” in terms of providing equal education to students with ethnically and racially diverse backgrounds. The reality was different. While my children and many white students took advanced classes in the gifted or honors track, a large number of minority students were in the lowest tier called “main stream.” A major reason for the difference is that some children were privileged and had the resources to succeed. Talented minority students with less than optimal resources and support from various societal stakeholders (including school counselors) are unlikely to perform as well as privileged children in seemingly “integrated” schools. They are less likely to get into top colleges and live up to their potential unless we give them adequate opportunities and support.
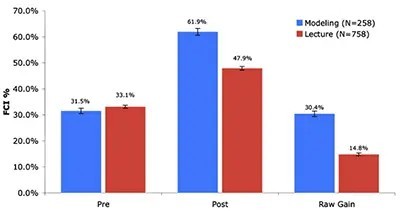
Now let’s go back to the question of the “unique” perspectives of students in a physics class. I wonder if the Chief Justice is assuming that all physics instructors must be a “sage on a stage,” and that students have nothing to contribute to the classroom dynamic. Research in physics education, including my own, shows that teaching by telling does not work for a majority of students; rather the physics instructor must actively engage students in the learning process in order for learning to be meaningful. For example, the photos above show students at Chicago State University, a minority serving institution on Chicago's South Side, engaged in active learning environments that have been shown to aid minority students develop a deep understanding of physics. The chart above shows the average scores of matched students before (pre) and after (post) instruction on a well-known standardized physics test called the Force Concept Inventory (FCI) for Modeling Instruction (a research-based approach to helping students learn in which students work in groups and build models to develop a good grasp of physics) and traditional lecture classes at Florida International University, also a minority serving institution. The chart shows that the average raw learning gains from pre-instruction to post-instruction on concepts related to force is significant higher for Modeling Instruction than for lecture classes. As the director of a center that focuses on supporting teaching innovation in the nine natural sciences departments at the University of Pittsburgh, I support faculty members who are excited about developing a classroom culture in which students are engaged in discussions with the instructor and their peers.
The Chief Justice may also be assuming that physics is just a collection of facts and equations and discussions of societal and real world issues do not have relevance in physics classes, so there would not be any need for a diversity of perspectives. This assumption is not correct. More than ever, physicists are focusing on the implications of their research to society and these thought processes are impacted by the perspectives of scientists with diverse backgrounds. For example, physicists from third world countries are more likely to be inspired to develop improved stoves, solar cells, water purification systems, or solar powered lamps.
Moreover, physics as a discipline prepares students for diverse careers and a majority of physics undergraduate majors who do not pursue a higher degree in physics typically find employment in diverse fields such as government, industry, K-12 education, or they pursue higher degrees in engineering, law, business and medicine. In fact, in the last few decades, a majority of physics Ph.Ds. (approximately 70 percent) have found employment outside academia. The enriching perspectives that diverse groups of students bring to physics classes shape the thought processes of all students who go into varied careers and impact innovation and progress in every walk of life.
We should all focus our effort on providing greater opportunities to students from underrepresented groups. Without figuring out ways to tap the potential of this large number of talented students, we risk losing our competitive edge.
References
AIP Statistical Research Center
W. Kamkwamba, The Boy Who Harnessed The Wind.
Chandralekha Singh
Chandralekha Singh is a professor of physics and the founding director of the Discipline-Based Science Education Research Center at the University of Pittsburgh.